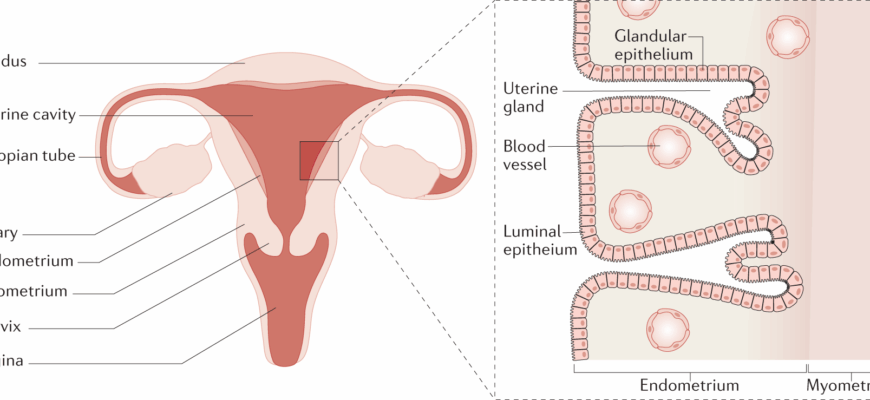
The endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus, plays a crucial role in womens reproductive health. It undergoes cyclical changes in response to hormonal fluctuations, which are essential for menstruation and pregnancy. However, when the endometrium becomes heterogeneous, it can signal underlying issues that may have significant health implications, including an increased risk of cancer.
- What is Heterogeneous Endometrium?
- Causes of Heterogeneous Endometrium
- Implications of a Heterogeneous Endometrium
- Endometrial Cancer Risks
- Diagnosis and Management
- Conclusion
- The Role of Lifestyle and Monitoring
- Regular Check-Ups: A Proactive Approach
- Hormonal Therapies: A Balancing Act
- Innovative Treatments on the Horizon
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatment
- Community Support and Awareness
What is Heterogeneous Endometrium?
A heterogeneous endometrium refers to variations in the thickness and texture of the endometrial lining. This condition is typically identified through imaging techniques such as ultrasound, where the lining appears irregular or mixed in echogenicity. While a homogeneous endometrium is smooth and uniform, a heterogeneous one may present as patchy or contain areas of differing density.
Causes of Heterogeneous Endometrium
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can lead to irregular endometrial growth.
- Endometrial Hyperplasia: An overgrowth of the endometrial cells can cause a thickened or heterogeneous lining.
- Endometrial Polyps or Fibroids: These benign growths can disrupt the uniformity of the endometrial layer.
- Chronic Endometritis: Inflammation of the endometrium can lead to structural changes.
Implications of a Heterogeneous Endometrium
While a heterogeneous endometrium can be benign, it may also indicate underlying pathology. The condition can lead to abnormal uterine bleeding, discomfort, and fertility issues. More importantly, it can be a precursor to more serious conditions, including endometrial cancer.
Endometrial Cancer Risks
The relationship between heterogeneous endometrium and cancer risk is complex. While not all cases lead to cancer, certain patterns and accompanying symptoms warrant further investigation:
- Persistent Thickening: Consistently thick or irregular endometrium over multiple menstrual cycles can be a red flag.
- Presence of Atypical Cells: Biopsy results showing atypical hyperplasia significantly increase cancer risk.
- Age and Menopausal Status: Women in perimenopause or postmenopause with heterogeneous endometrium have a higher risk due to prolonged estrogen exposure without progesterone counteraction.
Diagnosis and Management
Early detection and management of heterogeneous endometrium are vital in preventing progression to malignancy. Diagnostic approaches include:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Provides detailed images of the uterine lining to identify heterogeneity.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Essential for assessing cellular changes and ruling out malignancy.
- Hysteroscopy: Allows direct visual examination and biopsy of the uterine cavity.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve hormonal therapy to regulate menstrual cycles, surgical removal of polyps or fibroids, or more extensive interventions if precancerous or cancerous cells are detected.
Conclusion
A heterogeneous endometrium is more than just a variation in uterine lining texture; it can be a harbinger of significant health issues, including cancer. Awareness and timely medical attention are crucial. Women experiencing symptoms such as irregular bleeding should seek evaluation to ensure early detection and appropriate management. Through proactive monitoring and treatment, the risks associated with a heterogeneous endometrium can be effectively mitigated.
The Role of Lifestyle and Monitoring
Lifestyle factors can significantly influence the health of the endometrium. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking can help regulate hormonal levels and reduce the risk of endometrial abnormalities. Furthermore, women with a family history of endometrial or other related cancers should be more vigilant and consult with healthcare providers for personalized monitoring strategies.
Regular Check-Ups: A Proactive Approach
For women experiencing symptoms such as irregular bleeding or pelvic pain, regular gynecological check-ups are essential. These appointments provide an opportunity for early detection of changes in the endometrium. Regular ultrasounds and, if necessary, biopsies can help track any progression from benign to potentially malignant states, allowing for timely intervention.
Hormonal Therapies: A Balancing Act
Hormonal therapies can be effective in managing heterogeneous endometrium, especially when caused by hormonal imbalances. Progesterone therapy, for instance, can help counteract excessive estrogen and reduce the risk of hyperplasia. However, the decision to use hormonal treatments should always be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering potential side effects and individual health profiles.
Innovative Treatments on the Horizon
Advancements in medical research continue to offer new hope for managing endometrial health. Emerging treatments, such as targeted therapies and minimally invasive surgical techniques, provide less invasive options with quicker recovery times. These innovations are particularly beneficial for women at higher risk of cancer, offering effective management while preserving fertility whenever possible.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatment
The future of managing heterogeneous endometrium lies in personalized medicine. By understanding the genetic and molecular makeup of individual patients, healthcare providers can offer treatments tailored to specific needs, improving outcomes and reducing unnecessary interventions.
Community Support and Awareness
Raising awareness about the implications of a heterogeneous endometrium is crucial for early detection and prevention of potential complications. Support groups and community education programs can empower women with knowledge about their reproductive health, encouraging proactive health-seeking behaviors.
Ultimately, understanding and addressing the implications of a heterogeneous endometrium requires a multifaceted approach involving lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, medical interventions, and community support. By staying informed and engaged with healthcare providers, women can navigate these challenges with confidence and safeguard their reproductive health.
As the landscape of womens health continues to evolve, ongoing research and innovation remain vital in unraveling the complexities of the endometrium, ensuring that women have access to the best possible care and outcomes.

I appreciate the detailed explanation on how hormonal imbalances can affect the endometrial lining. The insights on potential cancer risks are particularly eye-opening and stress the importance of regular check-ups.
This article sheds light on an often overlooked aspect of women’s health. The discussion about potential causes like polyps or fibroids is very insightful, providing readers with a better understanding of their condition.
A well-written piece that highlights important aspects of women’s health. The connection between heterogeneous endometrium and cancer risk is explained thoroughly, emphasizing the need for medical attention if symptoms persist.
Very informative! I found the section on endometrial hyperplasia particularly enlightening. It’s great to see such comprehensive information available for those who might be experiencing similar symptoms.
The article does an excellent job of explaining complex medical terms in a way that is easy to understand. It’s a valuable resource for women looking to educate themselves about their reproductive health.
This article provides a clear and informative overview of the heterogeneous endometrium. It helps in understanding the potential causes and implications, which is crucial for anyone concerned about their reproductive health.